

What is a frog?
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (literally without tail in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" appeared in the early Triassic of Madagascar, but molecular clock dating suggests their origins may extend further back to the Permian, 265 million years ago. Frogs are widely distributed, ranging from the tropics to subarctic regions, but the greatest concentration of species diversity is in tropical rainforest. There are about 7,300 recorded species, which account for around 88% of extant amphibian species. They are also one of the five most diverse vertebrate orders. Warty frog species tend to be called toads, but the distinction between frogs and toads is informal, not from taxonomy or evolutionary history.
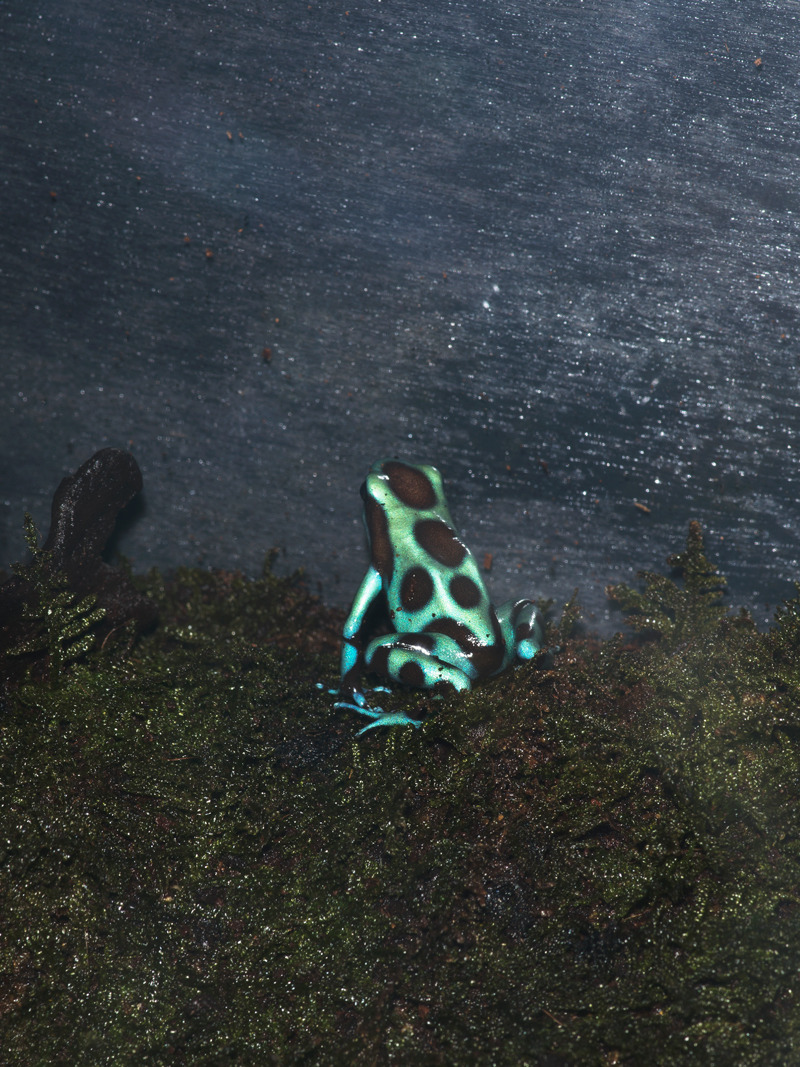
An adult frog has a stout body, protruding eyes, anteriorly-attached tongue, limbs folded underneath, and no tail (except in tailed frogs). Frogs have glandular skin, with secretions ranging from distasteful to toxic. Their skin varies in colour from well-camouflaged dappled brown, grey and green to vivid patterns of bright red or yellow and black to show toxicity and ward off predators. Adult frogs live in fresh water and on dry land; some species are adapted for living underground or in trees.
Frogs typically lay their eggs in water. The eggs hatch into aquatic larvae called tadpoles that have tails and internal gills. They have highly specialized rasping mouth parts suitable for herbivorous, omnivorous or planktivorous diets. The life cycle is completed when they metamorphose into adults. A few species deposit eggs on land or bypass the tadpole stage. Adult frogs generally have a carnivorous diet consisting of small invertebrates, but omnivorous species exist and a few feed on plant matter. Frog skin has a rich microbiome which is important to their health. Frogs are extremely efficient at converting what they eat into body mass. They are an important food source for predators and part of the food web dynamics of many of the world's ecosystems. The skin is semi-permeable, making them susceptible to dehydration, so they either live in moist places or have special adaptations to deal with dry habitats. Frogs produce a wide range of vocalizations, particularly in their breeding season, and exhibit many different kinds of complex behaviors to attract mates, to fend off predators and to generally survive.
Frogs have a highly developed nervous system that consists of a brain, spinal cord and nerves. Many parts of frog brains correspond with those of humans. It consists of two olfactory lobes, two cerebral hemispheres, a pineal body, two optic lobes, a cerebellum and a medulla oblongata. Muscular coordination and posture are controlled by the cerebellum, and the medulla oblongata regulates respiration, digestion and other automatic functions.
The eyes of most frogs are located on either side of the head near the top and project outwards as hemispherical bulges. They provide binocular vision over a field of 100° to the front and a total visual field of almost 360°. They may be the only part of an otherwise submerged frog to protrude from the water. Each eye has closable upper and lower lids and a nictitating membrane which provides further protection, especially when the frog is swimming. Members of the aquatic family Pipidae have the eyes located at the top of the head, a position better suited for detecting prey in the water above. The irises come in a range of colours and the pupils in a range of shapes. The common toad (Bufo bufo) has golden irises and horizontal slit-like pupils, the red-eyed tree frog (Agalychnis callidryas) has vertical slit pupils, the poison dart frog has dark irises, the fire-bellied toad (Bombina spp.) has triangular pupils and the tomato frog (Dyscophus spp.) has circular ones. The irises of the southern toad (Anaxyrus terrestris) are patterned so as to blend in with the surrounding camouflaged skin.
The distant vision of a frog is better than its near vision. Calling frogs will quickly become silent when they see an intruder or even a moving shadow but the closer an object is, the less well it is seen. When a frog shoots out its tongue to catch an insect it is reacting to a small moving object that it cannot see well and must line it up precisely beforehand because it shuts its eyes as the tongue is extended. Although it was formerly debated, more recent research has shown that frogs can see in colour, even in very low light.
- Wikipedia






